A Hofmann Elimination Results in Which of the Following
Which of the following reactions is Hofmann elimination. Benzoic acid and benzamide Ob 14-dicarboxylic acid of benzene and aniline OC 14-diamide of benzene and benzene od 14-dicarboxylic acid or.

What Is Hofmann Elimination Chemistry Questions
The unknown amine is.
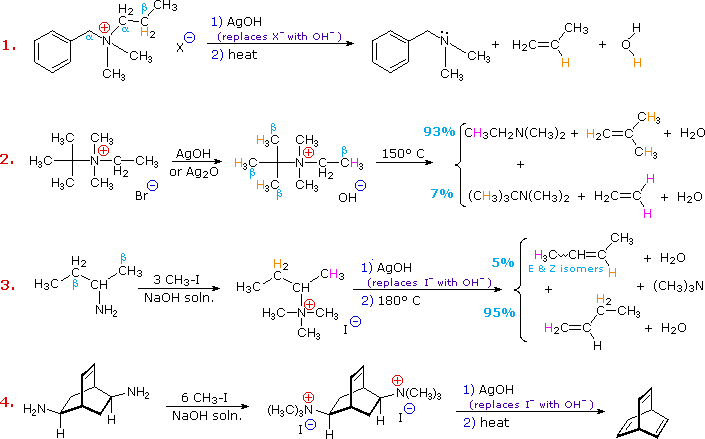
. The intermediate isocyanate can be trapped with various nucleophiles to form stable carbamates or other products rather than undergoing decarboxylation. The Hofmann Elimination results in the formation of the less substituted alkene. CH34NCl- Sec-Butylamine is the common name of what compound.
Deprotonation of water also takes place by silver oxide. It results in the formation of hydroxide ions. The least substituted alkene is the primary result in this reaction for example beginarraycc.
This reaction is known as Hofmann elimination. Elimination requires an _____ periplanar geometry where the β hydrogen and the NCH33 are oriented on opposite. The Hofmann exhaustive methylation mechanism starts with formation of the ammonium iodide salt then ammonium iodide salt reacts with silver oxide and gives silver iodide as precipitate.
The loss of the β-hydrogen occurs preferably from the most unhindered least substituted position -CH 3 -CH 2 -R -CH R 2. Example 1 is interesting in two respects. 14-diamide of benzene and benzene O d.
N-methyl-1-propanamine 2-butanamine N-methyl-2-propanamine 1-butanamine N. O True O False What are the structures of the two monomers needed to synthesize the following copolymer. Which of the following statements concerning NMR spectra of amines are correct.
O True O False What are the structures of the two monomers needed to synthesize the following copolymer. When tetraalkylammonium halide is heated with damp silver oxide it produces quaternary ammonium hydroxide which undergoes β-elimination to produce alkenes when heated to a high temperature. Hofmann elimination is an elimination reaction of an amineThe least stable alkene the one with the least number of substituents on the carbons of the double bond called the Hofmann product is formedThis tendency known as the Hofmann alkene synthesis rule is in contrast to usual elimination reactions where Zaitsevs rule predicts the formation of the most stable alkene.
Which of the following is the product of Hofmann elimination of. The Hofmann elimination proceeds via the E2 mechanism. C H X 3 C H X 2 N H X 2.
The product alkene with fewer substitutents will predominate. What product would result from the Hofmann elimination of the following quaternary ammonium hydroxide. C H X 2 C H N H C H X 3.
Unlike in other E2 mechanisms the base removes a proton from the _____ substituted β carbon. H₂C heat -OH CH CH3 CH3 O a CHE Oь. The overall result in a Gabriel synthesis is that a halogen X is replaced by -NH2.
The Hofmann elimination occurs via an _____ mechanism. CH3 Od HƏN CH3 Оe. H₂C heat -OH CH CH3 CH3 O a CHE Oь.
108d A Cope elimination requires the synthesis of N-oxides and these are usually formed by oxidation of the. Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. H o f f m a n n e l e m i n a t i o n is an organic reaction used to convert an amine with a.
Benzoic acid and benzamide Ob. Hofmann elimination is an elimination reaction of an amineThe least stable alkene the one with the least number of substituents on the carbons of the double bond called the Hofmann product is formedThis tendency known as the Hofmann alkene synthesis rule is in contrast to usual elimination reactions where Zaitsevs rule predicts the formation of the most stable alkene. C H X 2 C H N H X 2.
Start studying the Ochem 12B Ch19 Hmwk flashcards containing study terms like Provide the systematic name for the compound below. Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. Asked Nov 22 2018 in Chemistry by alam905 911k points Which of the following is the product of Hofmann elimination of.
The resulting products are trimethylamine and ethylene. Which of the following is the most effective hydride reducing agent in reductive amination reactions. C H X 3 C H X 2 N H C H X 3.
What product would result from the Hofmann elimination of the following quaternary ammonium hydroxide. What is Hofmann elimination. 1 Answer 1 vote.
The Hofmann Elimination results in the formation of the less substituted alkene. I tried to get the answer using concept of Hofmann elimination. Sodium hypochlorite lead tetraacetate N-bromosuccinimide and bistrifluoroacetoxyiodobenzene can effect a Hofmann rearrangement.
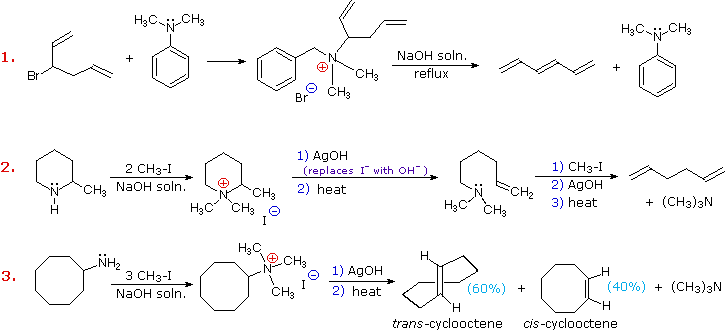
Hofmanns Rule implies that steric effects have the greatest influence on the outcome of the Hofmann or similar eliminations. Three additional examples of the Hofmann elimination are shown in the following diagram. -the overall result in a Gabriel synthesis is that a halogen X is replaced by -NH2.
It involves 3 steps. The amine is treated with silver oxide and water and then heated to 120 C. 14-dicarboxylic acid of benzene and aniline O c.
Second this salt is not converted to its hydroxide analog prior to elimination. Heating amine oxides to produce alkenes is known as Cope elimination 224108d104 and a typical reaction temperature is 120C significantly lower than that required for the Hofmann elimination as shown for the conversion of251 to252. First it generates a 4º-ammonium halide salt in a manner different from exhaustive methylation.


Comments
Post a Comment